AI + Human Quality Control is redefining how translation is done in 2026 by combining the speed of artificial intelligence with the judgment, cultural awareness, and subject-matter expertise of professional linguists. Instead of choosing between fast but risky machine translation or slow but expensive human-only workflows, organisations are increasingly adopting a hybrid model that delivers accuracy, scalability, and brand consistency simultaneously—an approach used by global language service providers like VerboLabs.
This shift is shaping how international businesses communicate, localize products, and maintain trust across languages without compromising quality.
What Is AI-Assisted Translation With Human Quality Control?
AI-assisted translation with human QC refers to a workflow where AI generates the initial translation, and trained linguists review, edit, and validate the output before delivery.
This approach is often referred to as Machine Translation Post-Editing (MTPE), but by 2026, it has evolved far beyond basic proofreading.
Understanding AI Translation
AI translation typically relies on neural machine translation (NMT) models that analyse massive datasets to predict the translation for a given sentence. These systems excel at:
- Processing large volumes of content quickly
- Maintaining baseline terminology consistency
- Delivering instant first drafts across dozens of languages
However, AI works statistically, not contextually. It doesn’t understand intent—it predicts language patterns.
What Human Quality Control Really Involves
Human Quality Control (QC) goes far beyond basic proofreading. Professional linguists:
- Refine tone, style, and brand voice
- Correct contextual or cultural misinterpretations
- Ensure industry-specific terminology accuracy
- Adapt content for local audiences (localization)
This process—often called Machine Translation Post-Editing (MTPE)—is where AI output becomes publication-ready.
Why the Hybrid Model Matters in 2026
Translation now combines both automated and human-generated content, which offers an accurate translation, but slow speed and with increasing expenses. Translations generated by machines have rapidly increased due to faster technological advances in computers; however, the risk associated with using machines for high-value or sensitive materials is extremely high.
Companies implementing these hybrid techniques benefit from a balance between speed and quality, reducing costs while maintaining high-quality standards, maintaining the consistency of their brand, and consistently reaching a global audience. This benefit translates into international brands and business will enabling the ability of company to sustain its future as an international brand.
Key Benefits of AI + Human Quality Control

Higher Accuracy and Cultural Relevance
Initially created with AI is a good draft, but having a human edit the following will help alleviate:
- Idiomatic phrases that fail to translate directly
- Cultural references that require modifications
- Subtle Differences In Provided Tone
AI produces a solid first draft, but humans catch:
- Idioms that don’t translate directly
- Cultural references that need adaptation
- Subtle tone mismatches
Scalable Global Communication
The use of combined workflows enables organisations to:
- Acquire the ability to accelerate the launch of multilingual websites.
- Update products simultaneously across more than one marketplace.
- Expand global growth rapidly.
Cost-Effectiveness Without Compromise
Through the reduction of the manual translation process:
- The costs associated with the translation process drop substantially
- Human resource conversion is focused on creating the highest level of value.
Consistency Across Content Types
Technical glossaries, style guides and QA checks need to be in place to ensure:
- Consistency of Technical Terminology
- Continuity of Brand Messaging
- Prevention of Errors When Expanded Globally
Where AI + Human QC Works Best

AI combined with human quality control performs best in high-volume, quality-sensitive content where speed alone is not enough.
Website & App Localization
The ability of AI to quickly translate a wide variety of UI components, including menus, error messages, and onboarding screens, has been further enhanced by human input. The role of people involves the following:
- Fixing any instances where awkward phrasing could have affected user experience.
- Ensuring phrases used in different cultures align with context (i.e. Call to Action language, form labels).
- Maintaining consistent use of phrasing across all screens/platforms.
Technical & Product Documentation
Repetitive forms of documents (like manuals and specifications) are produced efficiently with the assistance of AI, but should also be reviewed by Human QC for:
- Accurate terminology.
- Logical clarity of document content to be understandable by end users.
- Compliance with applicable industry standards.
Marketing & Brand Communication
Marketing content benefits immensely from the hybrid model:
- AI provides a base draft quickly
- Humans adapt emotional tone, humour, and persuasion
- Brand voice stays consistent across regions
Internal & Corporate Communication
Policies, training content, and leadership messaging require precision and neutrality. Human QC prevents
- Misinterpretation of policies
- Cultural insensitivity
- Legal ambiguity
Multimedia & Subtitling
AI does a great job of Conducting Transcription and Subtitle Generation, but it must have Human Quality Control Performed to:
- Ensure Proper Timing of Subtitles
- Ensure Readability of Subtitles
- Adapt Spoken Words into Written Form to Maintain Natural Flow
- Ensure Accessibility Standards Are Met
What AI Still Struggles With
Despite major advances, AI translation still has clear limitations.
Contextual Meaning
AI’s analysis of language is done statistically, not contextually. It is often confused by ambiguous phrases, does not comprehend implied meaning, and is unable to read emotional subtext.
Cultural Nuance
Cultural references, idioms, and social norms vary widely. AI may translate literally when adaptation is required.
Emotion, Humour, and Tone
Sarcasm, irony, humour, and persuasive language are especially challenging for AI because they rely on shared human experience.
High-Stakes Content
High-stakes content, such as medical, financial, legal, and regulatory content, requires an extremely high level of accuracy. Because of that, AI alone cannot assess the level of risk, liability, or ethicality associated with the content.
How the Translator’s Role Is Evolving
AI’s evolution has changed how translators work, but it has not increased the need for translators. Translators’ roles have evolved into a variety of new functions that keep pace with technological advancements:
- Refiners of AI-generated texts.
- Cultural adaptation of content.
- Expertise in proofreading and quality assurance processes.
- Management of global terminology and voice.
Rather than focus on repetitive tasks, translators can now use their expert judgement, analytical experience and decision-making skills, as these are the areas where human beings excel compared to machines.
AI + Human Quality Control Workflow (Step-by-Step)
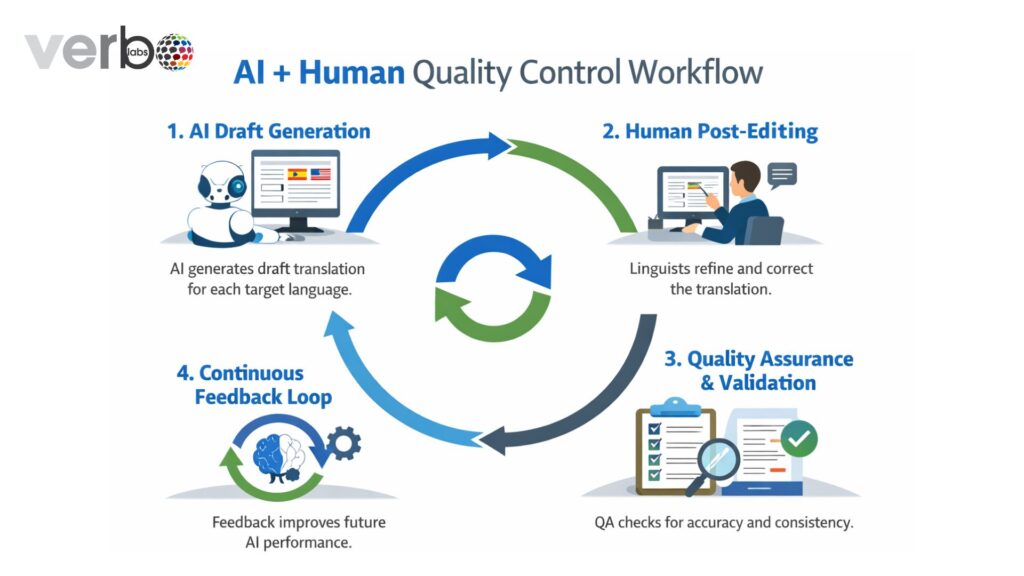
Step 1: AI Draft Generation
The AI system creates a draft translation quickly and in an organised way for each target language it needs to translate.
Step 2: Human Post-Editing
The professional linguists correct errors, adjust tone and style, apply glossaries and brand rules and improve readability and flow.
Step 3: Quality Assurance & Validation
QA checks include terminology consistency, formatting and layout accuracy, linguistic fluency, and compliance with style guides
Step 4: Continuous Feedback Loop
Human corrections feed back into the system, improving future AI outputs and reducing long-term effort.
How VerboLabs Implements AI + Human Quality Control
VerboLabs uses a structured hybrid approach designed for complex, real-world translation needs.
AI-Enhanced Translation Layer
VerboLabs uses AI translation to generate fast, consistent first-draft translations across multiple languages. By leveraging AI at the initial stage, large content volumes can be processed efficiently while maintaining terminology alignment and structural consistency from the outset.
Expert Human Linguists
Linguists systematically review and post-edit the machine-generated translation to ensure linguistic accuracy, tonal alignment, and contextual correctness. This process includes resolving meaning errors, refining sentence structure and flow, applying terminology rules, and validating that the final output reads naturally and appropriately for a native audience.
Localization & Cultural Adaptation
Beyond direct translation, content is culturally adapted to align with regional markets, user expectations, and communication norms. Through VerboLabs localization services, expressions, references, formats, and messaging are adjusted so the content remains relevant, contextually accurate, and appropriate for each target region.
Multi-Level Quality Assurance
Every project undergoes structured quality assurance checks using predefined glossaries, style guides, and automated QA tools. This process ensures terminology consistency, adherence to brand and linguistic standards, and a high level of linguistic accuracy before final delivery.
Multimedia & Advanced Formats
For audio, video, and multimedia content, AI is used for automated transcription and initial timing, while human specialists refine subtitles and scripts for linguistic accuracy, readability, timing precision, and cultural suitability. This ensures consistent, high-quality content across all multimedia formats.
Challenges of Hybrid Translation (and How to Solve Them)
Inconsistent AI Output
Solution: Create a structured quality control process on top of human review and supervise the use of the AI model.
Skill Gap in Post-Editing
Solution: Provide linguist training on the use of AI in workflow and in accordance with the company’s standards for machine translation post-editing.
Brand Voice Drift
Solution: Centralised style guides, glossaries, and brand language libraries.
Over-Reliance on Automation
Solution: Clear rules defining where human review is mandatory—especially for sensitive content.
The Future of Translation: Trends to Watch
In the development of the translation industry, by 2026, the main trends in development will be:
- Continuously learning AI using Human-in-the-loop.
- AI Technologies that are Domain-specific to the following Sectors – Legal, Medical, and Technical.
- Global Implementation of Adaptive Brand Languages.
- Hybrid Work Model is the Norm rather than an exception.
The Future is not simply automated but rather Collaboratively Intelligent.
Conclusion
AI + Human Quality Control is no longer an emerging concept—it has become the most reliable translation model in 2026. By combining the speed of AI with the judgment, cultural awareness, and domain expertise of human linguists, businesses can scale multilingual content without sacrificing accuracy, compliance, or brand credibility.
As global communication grows more complex, organisations that rely solely on automation risk inconsistency, misinterpretation, and loss of trust. Hybrid translation models solve this by ensuring every piece of content is fast, culturally appropriate, and fit for real-world use. This collaborative approach is not about replacing human expertise but amplifying it—allowing technology and linguists to work where each performs best.
For companies expanding across markets, AI with human quality control is no longer optional—it is the foundation of sustainable global communication. Providers like VerboLabs demonstrate how structured hybrid workflows can deliver translation that is scalable, accurate, and ready for high-impact business use.
Explore VerboLabs’ AI-powered, human-verified translation solutions and build multilingual content with confidence.

Explore VerboLabs’ expert AI + Human QC translation services and ensure accurate, culturally-ready content → Get Started
FAQs
It means AI creates the first translation draft, while human linguists review, refine, and validate it for accuracy, tone, and cultural relevance.
AI is fast but not fully reliable for nuance, emotion, or high-risk content. Human QC is still essential.
AI reduces manual workload, allowing human effort to focus only on refinement, lowering overall costs.
Websites, technical documentation, marketing content, internal communications, and multimedia projects.
Not consistently on its own. Human editors ensure tone, style, and brand identity remain intact.
Legal, medical, financial, and creative industries—and languages with strong cultural nuance.
Typically much faster than human-only translation, often reducing timelines by 30–50%.
Yes, but only with strict human review by domain-specialist linguists.



